LiDAR
This week in GIS applications we learned about LiDAR. LiDAR stands for "Light Detection and Ranging", and while it has been traditionally used in forestry science, as related to this week's lab topic, it is increasingly being used in archaeological research, which is my primary area of study.
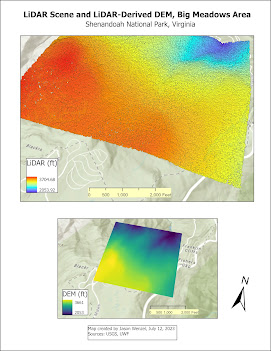
For this week's lab, we worked with LiDAR data from the Shenandoah National Park, Virginia, to examine tree height and tree canopy density. To do this, LiDAR data was obtained from the USGS in the form of an .las file, and then converted to a digital elevation model (DEM). To do this, I used the LAS Dataset to Raster tool in ArcGIS. This map shows the LiDAR point cloud along with DEM produced:
Next, I calculated forest height from the DEM and created a map from it along with an accompanying tree height chart:
Finally, I calculated biomass density by using the following tools in order: LAS to MultiPoint, Point to Raster, Is Null, Con, Plus, and Divide:
Overall, I found this week's lab very informative, yet challenging. I have not had much experience working with LiDAR data so there was a lot to learn in regards to basic terminology, methods of data collection and analysis, GIS integration, and map production.
As I mentioned above, LiDAR is increasingly being used in archaeological research, so I appreciate getting to engage with this type of data and learn how it used in GIS.


Comments
Post a Comment